Wet macular degeneration
Updated: 2023-02-21
Overview

Vision with macular degeneration
As macular degeneration develops, clear, typical vision (left) becomes impaired by a general haziness. With advanced macular degeneration, a blind spot forms at the center of the visual field (right).
Wet macular degeneration is a long-lasting eye disorder that causes blurred vision or a blind spot in the central vision. It's usually caused by blood vessels that leak fluid or blood into the macula (MAK-u-luh). The macula is the part of the retina that gives the eye clear vision in the direct line of sight.
Wet macular degeneration is one of two types of age-related macular degeneration. The other type, dry macular degeneration, is more common and less severe. The wet type always begins as the dry type.
Early detection and treatment of wet macular degeneration may help reduce vision loss. In some instances, early treatment may recover vision.
Symptoms
Wet macular degeneration symptoms usually appear suddenly and worsen quickly. They may include:
- Visual distortions, such as straight lines seeming bent.
- Reduced central vision in one or both eyes.
- The need for brighter light when reading or doing close-up work.
- Difficulty adjusting to low light levels, such as when entering a dimly lit restaurant or theater.
- Increased blurriness of printed words.
- Difficulty recognizing faces.
- A well-defined blurry spot or blind spot in the field of vision.
Macular degeneration doesn't affect side vision, so it doesn't cause total blindness.
When to see a doctor
See your eye doctor if:
- You notice changes in your central vision.
- You lose the ability to see fine detail.
These changes may be the first indication of macular degeneration, particularly if you're older than age 60.
Causes
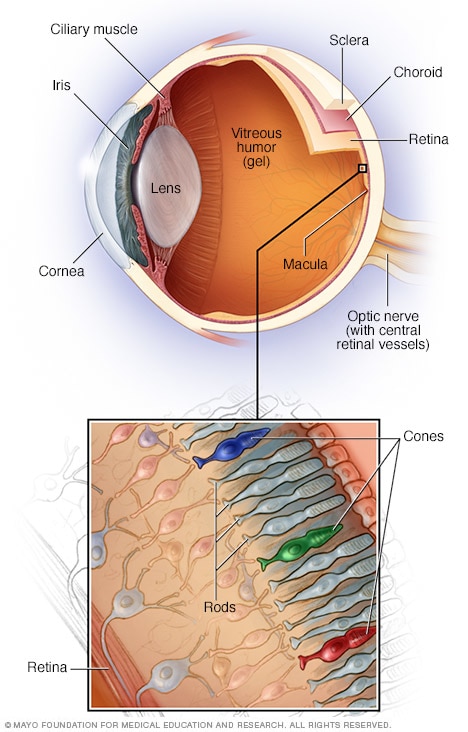
Parts of the eye
Your eye is a complex and compact structure measuring about 1 inch (2.5 centimeters) in diameter. It receives millions of pieces of information about the outside world, which are quickly processed by your brain.
No one knows the exact cause of wet macular degeneration, but it develops in people who have dry macular degeneration. Of all people with age-related macular degeneration, about 20% have the wet form.
Wet macular degeneration can develop in different ways:
- Vision loss caused by irregular blood vessel growth. Sometimes irregular new blood vessels grow from the choroid under and into the macula. This is known as choroidal neovascularization. The choroid is the layer of blood vessels between the retina and the outer, firm coat of the eye, called the sclera. These blood vessels may leak fluid or blood, affecting the retina's function.
- Vision loss caused by fluid buildup in the back of the eye. When fluid leaks from the choroid, it can collect between the thin cell layer called the retinal pigment epithelium and the retina or within the layers of the retina. This may cause irregularities in the macula layers, resulting in vision loss or distortion.
Risk factors
Factors that may increase your risk of macular degeneration include:
- Age. This disease is most common in people over 55.
- Family history and genetics. This disease has a genetic component. Researchers have identified several genes linked to the condition.
- Race. Macular degeneration is more common in white people.
- Smoking. Smoking cigarettes or being regularly exposed to tobacco smoke greatly increases your risk of macular degeneration.
- Obesity. Research indicates that being obese increases the chance that early or intermediate macular degeneration will progress to a more severe form of the disease.
- Cardiovascular disease. If you have diseases that affect your heart and blood vessels, you may be at higher risk of macular degeneration.
Complications
People whose wet macular degeneration has progressed to central vision loss have a higher risk of depression and social isolation. With profound loss of vision, people may see visual hallucinations. This condition is known as Charles Bonnet syndrome.
Prevention
It's important to have routine eye exams to identify early signs of macular degeneration. The following measures may help reduce your risk of developing wet macular degeneration:
- Manage all other medical conditions. For example, if you have cardiovascular disease or high blood pressure, take your medicine and follow your health care provider's instructions for controlling the condition.
- Don't smoke. Smokers are more likely to develop macular degeneration than nonsmokers. Ask your provider for help stopping smoking.
- Maintain a healthy weight and exercise regularly. If you need to lose weight, reduce the number of calories you eat and increase the amount of exercise you get each day.
- Choose a diet rich in fruits and vegetables. These foods contain antioxidant vitamins that reduce your risk of developing macular degeneration.
- Include fish in your diet. Omega-3 fatty acids, which are found in fish, may reduce the risk of macular degeneration. Nuts such as walnuts also contain omega-3 fatty acids.
Diagnosis
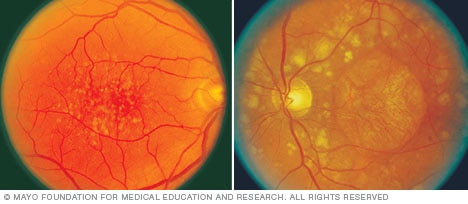
Drusen
The appearance of yellow deposits, called drusen, on color photographs of the retina indicates the development of early-stage dry macular degeneration (left). As the condition progresses to the advanced stage (right), the eye may lose light-sensitive cells that make up the macula. This is known as atrophy.
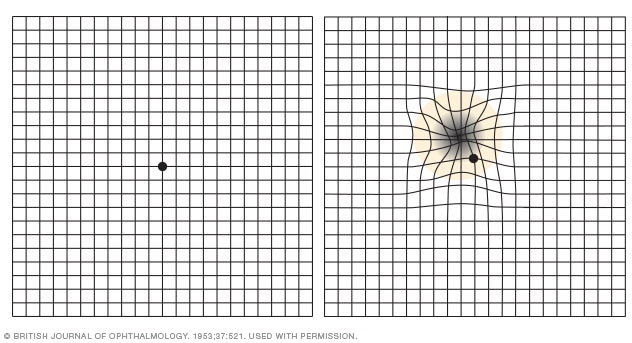
Amsler grid
Viewing an Amsler grid in an advanced stage of macular degeneration, you may see distorted grid lines or a blank spot near the center of the grid (right).
Your eye doctor reviews your medical and family history and conduct a complete eye exam. To confirm a diagnosis of macular degeneration, your eye doctor may suggest other tests, including:
- Examination of the back of your eye. Your eye doctor puts drops in your eyes to dilate them. Then a special instrument is used to examine the back of your eye. Your eye doctor looks for fluid or blood or a mottled appearance that's caused by yellow deposits that form under the retina, called drusen. People with macular degeneration often have many drusen.
- A test for changes in the center of your vision. During an eye exam, your eye doctor may use an Amsler grid to test for changes in your central vision. If you have macular degeneration, some of the straight lines in the grid may look faded, broken or distorted.
- Fluorescein angiography. During this test, your eye doctor injects a dye into a vein in your arm. The dye travels to and highlights the blood vessels in your eye. A special camera takes pictures as the dye travels through the blood vessels. The images will show if you have leaking blood vessels or retinal changes.
- Indocyanine green angiography. Like fluorescein angiography, this test uses an injected dye. It may be used to confirm the findings of a fluorescein angiography or to identify problem blood vessels deeper in the retina.
- Optical coherence tomography. This noninvasive imaging test displays detailed cross sections of the retina. It identifies areas of thinning, thickening or swelling. This test also is used to help monitor how the retina responds to macular degeneration treatments.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT) angiography. This is a newer, noninvasive test. In certain cases, OCT allows your eye doctor to see unwanted blood vessels in the macula. Though still used primarily as a research tool, its use is increasing in clinics.
Treatment
Treatments are available that may help slow disease progression and preserve existing vision. If started early enough, treatment may recover some lost vision.
Medications
Some medicines, called anti-VEGF drugs, may help stop the growth of new blood vessels. These medicines block the effects of growth signals the body sends to generate new blood vessels. They are considered the first line treatment for all stages of wet macular degeneration.
Medicines used to treat wet macular degeneration include:
- Bevacizumab (Avastin).
- Ranibizumab (Lucentis).
- Aflibercept (Eylea).
- Brolucizumab (Beovu).
- Faricimab-svoa (Vabysmo)
Your eye doctor injects these medicines into the affected eye. You may need shots every 4 to 6 weeks to maintain the beneficial effect of the medicine. In some instances, you may partially recover vision as the blood vessels shrink and your body absorbs the fluid under the retina.
Possible risks of eye shots include:
- Conjunctival hemorrhage.
- Increased eye pressure.
- Infection.
- Retinal detachment.
- Eye inflammation.
Therapies
-
Photodynamic therapy. This procedure is a possible treatment for the irregular blood vessel growth in wet macular degeneration. However, it is much less common than treatment with anti-VEGF shots.
During photodynamic therapy, your eye doctor injects a medicine called verteporfin (Visudyne) into a vein in your arm. The medicine then travels to blood vessels in your eye. Your eye doctor shines a focused light from a special laser on the problem blood vessels in your eye. This activates the verteporfin, causing the problem blood vessels to close. This stops the leakage.
Photodynamic therapy may improve your vision and reduce the rate of vision loss. You may need repeated treatments over time, as the treated blood vessels may reopen.
After photodynamic therapy, you'll need to avoid direct sunlight and bright lights until the drug has cleared your body. This may take a few days.
-
Photocoagulation. During photocoagulation therapy, your eye doctor uses a high-energy laser beam to seal problem blood vessels under the macula. This procedure helps stop the vessels from bleeding, with the aim of minimizing further damage to the macula. Even with this treatment, blood vessels may regrow, requiring further treatment. The laser also can cause scarring that creates a blind spot.
Few people who have wet macular degeneration get this treatment. It generally isn't an option if you have problem blood vessels directly under the center of the macula. Also, the more damaged your macula is, the lower the likelihood of success.
- Low vision rehabilitation. Age-related macular degeneration doesn't affect your side vision and doesn't cause total blindness. But it can reduce or eliminate your central vision, which is necessary for reading, driving and recognizing people's faces. It may help for you to get care from a low vision rehabilitation specialist, an occupational therapist, your eye doctor and others trained in low vision rehabilitation. They can help you find ways to adapt to your changing vision.
Lifestyle and home remedies
Even after receiving a diagnosis of wet macular degeneration, you can take steps that may help slow vision loss.
- Don't smoke. If you smoke, ask your health care provider for help quitting.
-
Choose a healthy diet. The antioxidant vitamins in fruits and vegetables contribute to eye health. Kale, spinach, broccoli, squash and other vegetables have high levels of antioxidants, including lutein and zeaxanthin. These nutrients may benefit people with macular degeneration.
Eating foods containing high levels of zinc also may be helpful for people with macular degeneration. These include high-protein foods, such as beef, pork and lamb. Nonmeat sources include milk, cheese, yogurt, whole-grain cereals and whole-wheat bread.
Another good choice is healthy unsaturated fat, such as in olive oil. And research studies have shown that a diet high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as in salmon, tuna and walnuts, may lower the risk of advanced macular degeneration. But the same benefit is not shown from taking omega-3 supplements, such as fish oil pills.
- Manage your other medical conditions. If you have cardiovascular disease or high blood pressure, for example, take your medicine and follow your health care provider's instructions for controlling the condition.
- Maintain a healthy weight and exercise regularly. If you need to lose weight, reduce the number of calories you eat and increase the amount of exercise you get each day.
- Have routine eye exams. Ask your eye doctor about the recommended schedule for follow-up exams. In between checkups, you can do a self-assessment of your vision using an Amsler grid.
Vitamin supplements
For people with intermediate or advanced disease, taking a high-dose formulation of antioxidant vitamins and minerals may help reduce the risk of vision loss. Research from the Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 (AREDS2) has shown benefit in a formulation that includes:
- 500 milligrams (mg) of vitamin C.
- 400 international units (IU) of vitamin E.
- 10 mg of lutein.
- 2 mg of zeaxanthin.
- 80 mg of zinc (as zinc oxide).
- 2 mg of copper (as cupric oxide).
Ask your health care provider if taking supplements is right for you.
Coping and support
Vision loss from macular degeneration can affect your ability to do things such as read, recognize faces and drive. These tips may help you cope with your changing vision:
- Ask your eye doctor to check your eyeglass prescription. If you wear contacts or glasses, be sure your prescription is up to date. If new glasses don't help, ask for a referral to a low vision specialist.
-
Use magnifiers. A variety of magnifying devices can help you with reading and other close-up work, such as sewing. Such devices include hand-held magnifying lenses or magnifying lenses you wear like glasses.
You also may use a closed-circuit television system that uses a video camera to magnify reading material and project it on a video screen.
- Change your computer display and add audio systems. Adjust the font size in your computer's settings. And adjust your monitor to show more contrast. You also may add speech-output systems or other technologies to your computer.
- Use electronic reading aids and voice interfaces. Try large-print books, tablet computers and audiobooks. Some tablet and smartphone apps are designed to help people with low vision. And many of these devices now come with voice recognition features.
- Select special appliances made for low vision. Some clocks, radios, telephones and other appliances have extra-large numbers. You may find it easier to watch a television with a larger high-definition screen, or you may want to sit closer to the screen.
- Use brighter lights in your home. Better lighting helps with reading and other daily activities, and it also may reduce the risk of falling.
- Consider your transportation options. If you drive, check with your doctor to see if it's safe to continue doing so. Be extra cautious in certain situations, such as driving at night, in heavy traffic or in bad weather. Use public transportation or ask a friend or family member to help, especially with night driving. Or use local van or shuttle services, volunteer driving networks, or rideshares.
- Get support. Having macular degeneration can be difficult, and you may need to make changes in your life. You may go through many emotions as you adjust. Consider talking to a counselor or joining a support group. Spend time with supportive family members and friends.
Preparing for an appointment
You will likely need a dilated eye exam to check for macular degeneration. Make an appointment with a doctor who specializes in eye care, such as an optometrist or an ophthalmologist. An eye doctor can perform a complete eye exam.
What you can do
Before your appointment:
- When you make the appointment, ask if you need to do anything to prepare.
- List any symptoms you're experiencing, including those that seem unrelated to your vision problem.
- List all medicines, vitamins and supplements you take, including doses.
- Ask a family member or friend to go with you. Having your pupils dilated for the eye exam will affect your vision for a time afterward, so you may need someone to drive or be with you after your appointment.
- List questions to ask during your appointment.
For macular degeneration, questions to ask include:
- Do I have dry or wet macular degeneration?
- How advanced is my macular degeneration?
- Is it safe for me to drive?
- Will I experience further vision loss?
- Can my condition be treated?
- Will taking a vitamin or mineral supplement help prevent further vision loss?
- What's the best way to monitor my vision for any changes?
- What changes in my symptoms should I call you about?
- What low vision aids might be helpful to me?
- What lifestyle changes can I make to protect my vision?
What to expect from your doctor
Your eye doctor is likely to ask you a number of questions, such as:
- When did you first notice your vision problem?
- Does the condition affect one or both eyes?
- Do you have trouble seeing things near you, at a distance or both?
- Do you smoke or did you used to smoke? If so, how much?
- What types of foods do you eat?
- Do you have other medical problems, such as high cholesterol, high blood pressure or diabetes?
- Do you have a family history of macular degeneration?